Medieval Art of Lady Looking at a Castle at Night
Medieval castles are ane of the almost iconic buildings of the Middle Ages , especially in Western Europe. During this menstruum, the castle served generally every bit the residence of a king, or the lord of the territory in which it was built. Therefore, the castle was the center of secular ability, and some elements of these structures were designed to reverberate this power.
Incidentally, the cathedral may be considered to exist the castle'south spiritual counterpart. In order to adequately protect the secular rulers living in them, castles were built as defensive structures. Over the course of the medieval period, castles had to make adaptations that allowed them to deal more finer with changes in siege warfare. True castles became obsolete during the 15 th century, when artillery became powerful enough to breach the rock walls of castles.
Origins of Medieval Castles
The origins of medieval castles have been traced to the nine thursday and x thursday centuries AD. One of the factors that led to the emergence of these structures is the collapse of the Carolingian Empire, which ruled over Central and Western Europe during its height of ability.
When the empire collapsed, these territories were no longer controlled past a key authorities, and was divided between local lords and princes. These rulers synthetic castles, which served as their private residence, and allowed them to assert their authority on the surrounding expanse. In addition, castles could exist used every bit offensive structures equally well, i.due east. as secure bases from which raids could be launched on the territory of rival nobles.
The earliest type of castle in medieval Europe is the motte-and-bailey castle. This blazon of castle originated in northern France during the ten th century, but soon spread to other parts of Europe as well. By the post-obit century, the motte-and-bailey was the most common form of castle in Europe, with the exception of Scandinavia. As its name suggests, this type of castle consists of two distinct elements – the motte and the bailey.
The Motte and Bailey Castle
The motte is a mound, either a natural or artificial one. In the latter case, the mound could exist created using globe taken from a ditch dug around the motte, or the whole castle. Some castles, like Lewes Castle and Lincoln Castle, accept two mottes. The mound was topped by a tower called a keep, which was initially congenital of woods.

Left: Reconstructed wooden go along at Lütjenburg, Germany, to show what they would have looked like. ( Public domain ). Right: Lincoln Castle, Britain, built in the 11th century by William the Conqueror on the site of existing Roman fortifications. ( Colin & Linda McKie / Adobe stock)
Later on, yet, medieval castles were congenital of stone, which is a more durable cloth. Stone castles, however, required considerably more time and manpower to construct. Some keeps consisted of several stories, the lowest 1 being used for services, such every bit storage or kitchen facilities. The primary reception area, or peachy hall, was located on the adjacent story, whilst the top story housed the lord's private apartments.
The second element of the castle, the bailey, is an enclosed courtyard congenital side by side to the motte. In some castles, the motte may take several baileys. This is seen, for case, in Warkworth Castle and Windsor Castle , both of which are in England. The bailey was protected by a wooden palisade, which was in plough surrounded by a ditch.

The Long Walk and Windsor Castle. ( Chris Lofty / Adobe stock)
Like the go along, wooden palisades were later replaced by stone walls. The bailey was the area occupied by vassals in the service of the castle's lord. This area usually included a blacksmith, a miller, and about of the necessary craftsmen of the period. The bailey was continued to the motte via a wooden drawbridge, which could be separated from the bailey as a last resort in the event of a siege.
The Normans and their Castles
An example of a motte-and-bailey castle is Durham Castle, a UNESCO Globe Heritage site in northeast England. This castle was originally constructed during the late 11 th century under the orders of William the Conqueror , the first Norman male monarch of England.

Durham Castle. ( immigrant1992 / Adobe stock)
The Normans had conquered England following their victory at the Boxing of Hastings in 1066. Nevertheless, in the early days of Norman dominion, there were still pockets of resistance around the land, which caused the Normans to send their troops effectually the country. They brought the motte-and-bailey castle from their homeland to England, and these, which were congenital of timber, could be erected in a matter of weeks, thus allowing them to quickly assert control over the land. It is estimated that the Normans synthetic over thousand wooden motte-and-bailey castles throughout England.
Subsequently, the Normans began using rock for the structure of their castles. Rock is a much stronger material than forest, hence increasing the defensive capabilities of medieval castles. In addition, stone castles were imposing monuments that functioned every bit symbols of Norman power in the state. It was a way for the Normans to stamp their mark on both the landscape and the hearts of their subjects. The motte-and-bailey castle eventually lost its popularity, and was replaced by a new type of castle.
Emergence of the Rock Keep Castle
Although motte-and-bailey castles were nonetheless being built during the eleven th century, a new type of castle, i.e. the stone proceed castle, was emerging in the same century. As suggested by its name, the primary component of the new form of castle is the keep. This structure is similar to that of its predecessor, in that it is a fortified tower equanimous of several stories.
The kitchens were located on the footing flooring, whilst living quarters were on the upper ones. The keep could be accessed via a flying of stairs, which led to the first story. Some keeps were surrounded by defensive walls, whilst others were built into the walls themselves. Initially, these keeps had a square design, but was later replaced with a circular one. The latter was an improvement, since information technology fabricated towers more resistant to siege applied science. The area within the walls of the castle remained as the bailey.
The Tiptop of Concentric Castles
Medieval castles' blueprint reached its pinnacle with the development of the concentric castle during the 12 th and thirteen thursday centuries. Simply speaking, a concentric castle is "a castle with two or more than concentric curtain walls, where the outer wall is lower than the inner and tin be defended from it." The walls not only provided the castle with multiple layers of defense, just also immune the defenders to inflict the maximum amount of impairment on the besiegers.
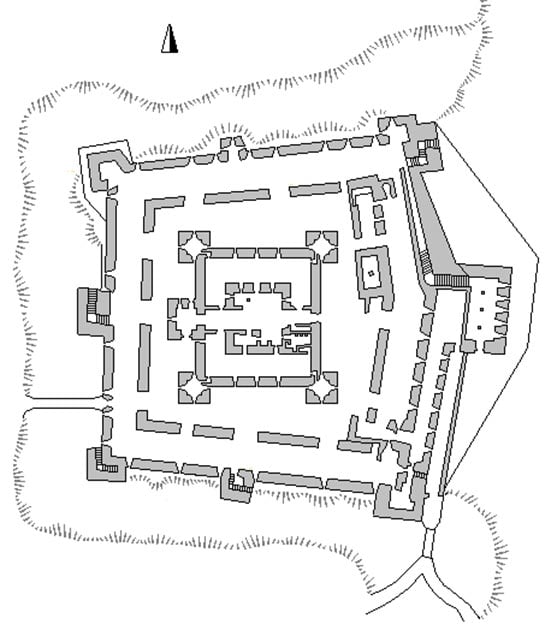
Program of Belvoir Castle / Fortress showing the typical blueprint of a concentric castle with a number of walls. ( CC BY-SA iii.0 )
The area in between ii walls was known also as the 'death hole', and attackers trapped within it were almost certain to be killed by the defenders. In improver to the concentric walls, these castles were as well oft equipped with various kinds of defensive features, such as crenellations, towers, and arrow slits, which further aided the defenders in the event of a siege. The concentric castle is believed to have a different origin from the two other castle types that take been mentioned.
It has been suggested that the concentric castle has its origins in the castra (singular castrum), significant 'fortified places') of ancient Rome. Whilst the keep was the principal defensive characteristic of the first ii types of castles, the castrum focused its defence force on walls and towers placed at regular intervals.
As an bated, the word 'castle' is derived from the Latin castellum, a diminutive of castrum. Information technology is believed that the concentric castle start appeared in the Middle East during the time of the Crusades, every bit a response to the advances made in siege technology in the region during that fourth dimension. The design arrived in Europe during the 13 thursday century, maybe brought back past returning crusaders.
Famous Concentric Castles
Belvoir Fortress, located in present-day Israel, only xx km (12.43 mi) south of the Sea of Galilee, is considered to be the earliest case of a concentric castle. Originally, the site was owned by a French nobleman past the proper noun of Velos, who lived in Tiberias. In 1168, Velos sold his property to the Knights Hospitaller, who immediately began building a castle, i.e. Belvoir Fortress, to defend the area.

The remains of Belvoir Castle. Annotation the two circuits of defensive wall, one inside the other. (AVRAMGR / CC By-SA four.0 )
In 1180, the castle successfully withstood a siege by Muslim forces. After the crushing defeat of the crusaders past Saladin at the Boxing of Hattin, Belvoir Fortress was besieged once again. The defenders of the castle held out for a year and a half, but finally surrendered in early on 1189. Although the castle has since fallen into ruins, its rectangular layout, which has been described as "ane castrum nested inside another", is still conspicuously visible.
One of the best-examples of a concentric castle in the Middle Eastward, however, is Krak des Chevaliers, in modern Syria. The electric current castle, like Belvoir Fortress, was constructed by the Hospitallers during the 12 th century.
Krak des Chevaliers is a massive fortress. The rock inner wall, for instance, is over iii m (ix.8 ft) thick, and is studded with seven towers, each having a diameter of 10 m (32.8 ft). The castle could accommodate a garrison of up to 2000 men, and had a stable for up to 1000 horses. In the result of a siege, the supplies in its 120 m (393.7 ft) long storeroom could keep the defenders going for up to five years. Krak de Chevaliers' defenses were further enhanced by its location, i.e. on a 650 m (2132.6 ft) colina that overlooked the surrounding area.

Krak des Chevaliers overlooking the surrounding expanse. (Nev1 / CC Past 2.0 )
Co-ordinate to one legend, when Saladin besieged Krak de Chevaliers in 1188, he captured the castle'southward commander, and ordered him to command the defenders to open the gates. The commander did so, and shouted the order in Standard arabic. Immediately later that, even so, he told his men, in French, to defend the castle to the concluding man. Krak des Chevaliers somewhen savage in 1271 to the Mamluks. A forged letter, allegedly from the Grand Chief of the Knights Hospitaller in Tripoli was sent to the castle, allowable the defenders to surrender the castle to the Mamluks, which they did.
Although the concentric castle was the most advanced fortification of its time, information technology was also extremely expensive, and fourth dimension-consuming to build. The construction of Krak des Chevaliers, for instance, took virtually three decades to complete. Therefore, just wealthy and powerful orders, similar the Knights Hospitaller , or monarchs, like the English language king, Edward I, were able to afford to build (and maintain) them. The fortifications built past the latter during his Welsh campaign are some of the finest examples of concentric castles in Europe.
One of these is Beaumaris Castle, whose construction began in the late xiii th century, simply came to a halt during the 1320s. The castle was never completed due to the lack of funds, and troubles brewing in Scotland. Still, it is a sight to behold, both for its calibration and ambition. One of the most remarkable aspects of the unfinished castle is its regular, almost square layout. Unlike Krak des Chevaliers, Beaumaris Castle was constructed on a evidently, and therefore required walls and towers facing in all directions, hence its layout.

Beaumaris Castle in Anglesey in Wales. ( WebStudio / Adobe stock)
- 1 of the Largest Castles in Europe Was Born to Resist the Mongol Invasion
- The Dramatic and Bloody History of Nottingham Castle
- Conwy Castle: This Fine Medieval Welsh Castle was Congenital for a Ferocious English language King
Gunpowder Inverse the Game
The introduction of gunpowder in Europe during the xiv th century would transform the way wars were fought on the continent. For the time beingness, however, the castle was non affected past this new weapon, equally early arms was not powerful enough to breach their stone walls. The situation, however, changed in the post-obit century, castles were no longer strong plenty to withstand artillery.
In 1494, for case, when the First Italian War broke out, the invading French army included a powerful artillery train, which allowed Charles VIII to hands destroy the castles of his enemies. No dubiousness, changes were fabricated to the castles, so as to allow them to withstand artillery attack. These changes, however, resulted in the conversion of castles to purely military machine structures, without its residential function. Therefore, the castle may exist regarded to have get obsolete by this point of fourth dimension.
Although medieval castles became obsolete by the 15 th century, they never disappeared from either the landscape or the popular imagination. Whilst some castles were abased in the centuries that followed, others continued to serve one role or another. Durham Castle, for case, remained the palace of the Bishop of Durham until 1832, when his residence was moved to Auckland Castle. Later, the castle was donated to Durham Academy, and its keep redeveloped for student accommodation.
Castles, including their ruins, have besides become tourist attractions, thanks to public fascination with castles, and the Middle Ages in general. Furthermore, the cultural and historical significance of many medieval castles have been recognized, resulting in their inscription on UNESCO's World Heritage List.
Elevation epitome: Medieval castles emerged in the 9 thursday century AD and became almost obsolete by the fifteen th century, but why did this happen? Source: Sergio / Adobe stock
By Wu Mingren
References
Crowther, D., 2018. Medieval Castles. [Online]
Bachelor at: https://thehistoryofengland.co.uk/resource/medieval-castles/
Durham Earth Heritage Site, 2020. The Motte and Bailey Castle. [Online]
Bachelor at: https://www.durhamworldheritagesite.com/architecture/castle/motte-and-ba...
English Heritage, 2020. Medieval Castles. [Online]
Available at: https://world wide web.english-heritage.org.britain/learn/histories/medieval-castles/
History on the Internet, 2020. Concentric Castles. [Online]
Bachelor at: https://www.historyonthenet.com/concentric-castles
History on the Net, 2020. Stone Proceed Castles. [Online]
Available at: https://world wide web.historyonthenet.com/stone-keep-castles
History on the Net, 2020. The Medieval Castle: 4 Dissimilar Types. [Online]
Available at: https://www.historyonthenet.com/medieval-castle
Kalif Publishing, 2018. Types of Castles. [Online]
Available at: http://medievalcastles.stormthecastle.com/essays/the-types-of-castles.htm
Ramsay, W., 1875. Castra. [Online]
Available at: http://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/secondary/SMIGRA*/Cast...
Rickard, J., 2014. The Italian Wars, 1494-1559. [Online]
Available at: http://world wide web.historyofwar.org/manufactures/wars_italian_wars.html
stanestane, 2020. Krak des Chevaliers. [Online]
Bachelor at: https://www.atlasobscura.com/places/krack-des-chevaliers
The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica, 2020. Castle. [Online]
Bachelor at: https://www.britannica.com/technology/castle-architecture
Tourist Israel, 2020. Belvoir Fortress. [Online]
Available at: https://www.touristisrael.com/belvoir-fortress/15970/
UNESCO, 2020. Crac des Chevaliers and Qal'at Salah El-Din. [Online]
Bachelor at: https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/1229/
UNESCO, 2020. Durham Castle and Cathedral. [Online]
Available at: https://whc.unesco.org/en/listing/370/
Welsh Authorities, 2019. Beaumaris Castle. [Online]
Available at: https://cadw.gov.wales/visit/places-to-visit/beaumaris-castle
www.castlesandmanorhouses.com, 2014. Castles. [Online]
Available at: http://www.castlesandmanorhouses.com/castles.htm
www.lordsandladies.org, 2017. Concentric Castles. [Online]
Bachelor at: http://www.lordsandladies.org/concentric-castles.htm
Source: https://www.ancient-origins.net/history-ancient-traditions/medieval-castles-0013422
0 Response to "Medieval Art of Lady Looking at a Castle at Night"
Post a Comment