what infection spreads from one area of infection to set up other areas of infection in the body?
Bacterial Skin Infections: Impetigo and MRSA
What kinds of bacteria tin cause contagious skin infections?
Sure leaner commonly alive on the skin of many people without causing damage. However, these bacteria can cause skin infections if they enter the trunk through cuts, open up wounds, or other breaks in the skin. Symptoms may include redness, swelling, pain, or pus.
How serious are bacterial skin infections?
While many bacterial peel infections are mild and easily treatable, some can become very serious and even life threatening. In addition, some bacterial infections can be spread to others. This is why prevention is so important.
What are the 2 nearly common bacteria that cause pare infections?
- Group A Streptococcus (GAS), often chosen "strep."
- Staphylococcus aureus, commonly called "staph."
Impetigo
What is impetigo?
Impetigo is a common bacterial skin infection caused by Group A Streptococcus (GAS) or "strep."
What is Group A Streptococcus (GAS)?
Grouping A Streptococcus (GAS) or "strep" is a common bacterium (bacterium is the singular form of the plural, bacteria) that is establish on the skin or in the throat ("strep pharynx"). People tin can carry GAS and have no symptoms of affliction or they may develop relatively mild skin infections, including impetigo.
How does impetigo spread?
Grouping A Streptococcus (GAS) or "strep" can be transmitted through direct person-to-person contact with someone who has the infection. GAS can also be picked up indirectly through contact with an item (such as a wrestling mat, gear, towel, razor, or cell phone) that is contaminated with the bacterium.
What are the symptoms of impetigo?
- Symptoms commonly began 1-3 days afterwards infection.
- Sores (lesions) begin as small red spots, usually on the face (especially around the nose and oral fissure), but can appear anywhere on the body.
- The sores are oftentimes itchy, but ordinarily not painful.
- The sores develop into blisters that break open up and ooze fluid -- this fluid contains infectious leaner that tin infect others if they take contact with it.
- Afterward a few days, the ruptured blisters form a flat, thick, honey-colored (yellow-brown) crust that eventually disappears, leaving red marks that heal without scarring.
- There may be bloated glands (enlarged lymph nodes), merely usually no fever.
- Click hither to view a photo of impetigo on the face up from DermAtlas.
What should athletes do if they think they have impetigo?
While balmy cases of impetigo may exist treated without seeing a health care provider, athletes are recommended to accept a medical professional decide what blazon of infection they take, how to treat it, and if it is contagious. If the infection is contagious, athletes should not practise or compete until their medical provider clears them to return.
Back to Peak
Back to Table of Contents
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
What is Staphylococcus aureus?
Staphylococcus aureus ("staph") is a bacterium that is carried on the pare or in the olfactory organ of approximately 25% to thirty% of healthy people without causing infection -- this is called colonization. Staph leaner are ane of the most common causes of skin infections in the U.S. Most of these skin infections are minor (such every bit pimples and boils), are not spread to others (not infectious), and usually can be treated without antibiotics. Nonetheless, some staph leaner are resistant to certain antibiotics -- 1 type is chosen MRSA.
What is MRSA?
MRSA stands for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. MRSA is a staph bacterium that sure antibiotics in the penicillin family should be able to treat, but cannot. When the infection is resistant to the medication, information technology is called resistance. However, other non-penicillin antibiotics tin effectively care for nearly MRSA infections.
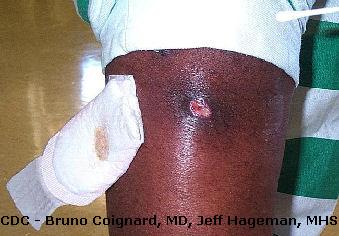 |
| MRSA Infection on Arm |
What causes antibiotic resistance?
Most resistance to antibiotics develops from taking them improperly. Examples are:
- Incomplete use: Not finishing the entire antibiotic prescription (oft because people start to feel better and terminate taking the medication).
- Inappropriate use: Taking antibiotics for a viral infection (antibiotics do Non treat viral infections such as colds or the flu).
- Unnecessary utilize: Taking antibiotics "only in example" (for case, taking them prior to a holiday or special event to try to foreclose illness).
It is important to take prescription medication merely when prescribed for you by a wellness professional and to accept all the medicine even if you feel better earlier you take completed the prescription.
How serious is MRSA?
Although health care providers can treat nearly MRSA skin infections in their offices, MRSA can be very serious and even cause death. MRSA can cause pneumonia or astringent infections of the blood, basic, surgical wounds, centre valves, and lungs. MRSA can exist fatal if not identified and treated with effective antibiotics.
How does someone get MRSA infection?
Nearly oft, MRSA is transmitted by direct skin-to-pare contact with someone who has the infection.
MRSA can exist spread by indirect contact too (for instance contact with a mat that has infected drainage on it or by sharing a towel or cell phone with someone who has MRSA). Because of this, never share personal hygiene and health items.
Where on the pare does MRSA appear and what are the symptoms?
MRSA infections usually occur where there is a pause in the skin (for example, a cut or wound), peculiarly in areas covered past hair (for example, the beard area, back of the neck, armpit, groin, legs, or buttocks)
MRSA may wait like a crash-land on the skin that may be ruby-red, swollen, warm to the touch, painful, filled with pus, or draining. The pus or drainage contains the infectious bacteria that can be spread to others. People with MRSA may take a fever.
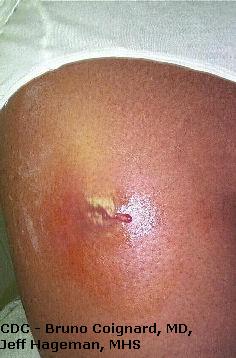 |
| MRSA Infection on Thigh |
How is MRSA diagnosed and treated?
Depending on your symptoms, your wellness care provider may send a nasal swab or skin tissue specimen to a laboratory to identify the infection or confirm that you accept MRSA.
Your wellness care provider may drain the pus from the lesion -- exercise not do this yourself.
If you are prescribed an antibiotic, have it exactly every bit directed and take all of the medicine even if the infection improves or goes away earlier you have finished the unabridged prescription. If the infection does not begin to better inside a few days, contact your health care provider.
Back to Elevation
Back to Table of Contents
Source: https://www.health.ny.gov/diseases/communicable/athletic_skin_infections/bacterial.htm
0 Response to "what infection spreads from one area of infection to set up other areas of infection in the body?"
Post a Comment